The involvement of Rhopr-CRF/DH in feeding and reproduction in the blood-gorging insect Rhodnius prolixus
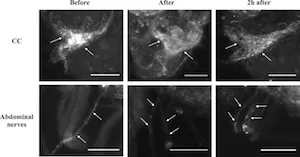
Graduate student Shirin Mollayeva (Lange Lab) recently published a paper entitled “The involvement of Rhopr-CRF/DH in feeding and reproduction in the blood-gorging insect Rhodnius prolixus” in General and Comparative Endocrinology. The kissing bug transmits the parasite that causes human Chagas disease through its urine while feeding on blood. We know that the hormone Rhopr-CRF/DH influences urination after eating, but it also appears to affect female reproduction -- suggesting a more complex role in the insect’s body. By injecting this hormon into kissing bugs, Shirin and colleagues showed that it actually reduces both the appetite and egg laying of kissing bugs. Their study might help control Chagas disease by providing a drug target to alter feeding, peeing and laying eggs.
Congrats to Shirin!
